Pellet Mills: Pelletizing equipment for the manufacture of wood and feed pellets.
Click on Links Below for Detailed Info.
Functional Description:
Pellet mills for feed mills, sometimes referred to as pellet presses or pellet press, are used to manufacture pellets for animal feed including fish food (aquafeed) from prepared feedstock grains (alfalfa, barley, corn, malt, oats, soybean, etc.). Pellet mills vary in size from 3 kilowatt to 375 kilowatt (5 horsepower to 500 horsepower) or larger. Production volume of pellets per pellet mill can range from 90 kilograms per hour to 8 tonnes per hour (200 pounds to 9 tons). Loose feedstock will be compacted from about 100 kg/m3 to 650 kg/m3 (6.5 lb/ft3 to 40.5 lb/ft3) providing an extremely dense and efficient product.
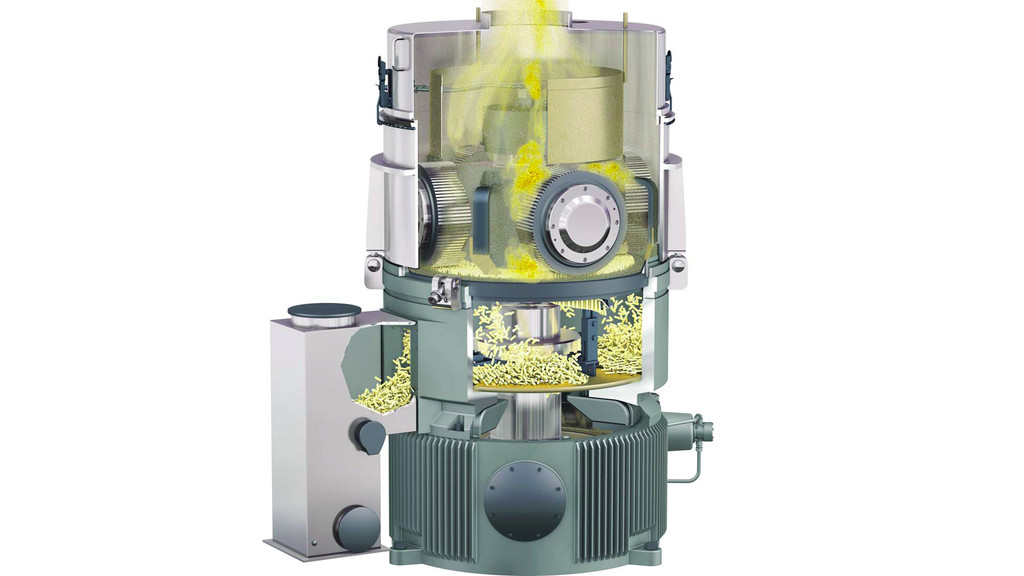
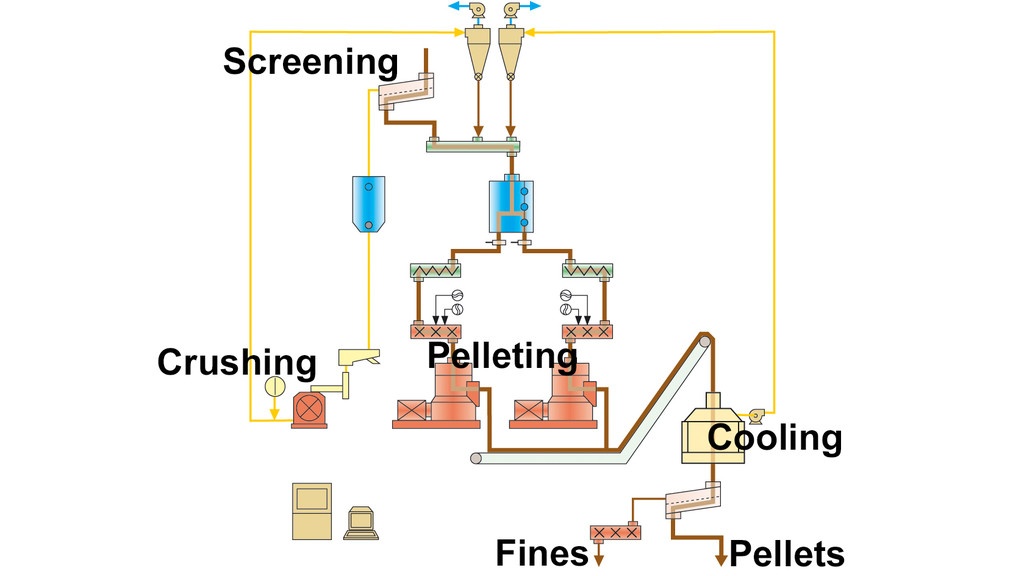
The pellets are made by compacting the feedstock through small holes in a die. The die holes are round and the pellets are pushed from the inside out by rollers. The pellets are formed as a continuous “rod” and cut to length by a knife at the periphery of the die.
Pellet mills have one or more conditioning units mounted above where liquids can be added to improve pelletability. Water is sometimes added in the form of steam resulting in firmer pellets.
From the conditioner, the feed stock falls into the centre of the pellet mill. In the pellet mill, rollers and feed ploughs push the material through the holes of the die plate. The die plate is either stationary and rollers rotate around the inner surface of the die, or the die rotates around the rollers. Outer knives cut the pellets to length.
There are generally two types of dies in the pellet mill – flat die or ring die. Die hole sizes usually range from approximately 2 mm (.050”) up to 10 mm (.400”). The thickness of the die plate helps to determine the compactness and stability of the pellet. Pellet dies vary in thickness up to approximately 100 mm (4”) thick. Pellet mill dies are usually manufactured from metal alloys, stainless steel or high chrome. Pressures in the die can reach up to 172,000 kPa (25,000 psi).
In a pellet plant, the pellets are transferred from the pellet mill, to a cooler/drier to remove the heat which is generated during the pelleting process. The moisture content of the pellets also needs to be reduced for durability during storage and shipping. Pellets are then normally stored in silos or bins for bulk shipping or to be processed by packaging systems.
The pellets produced by pelletizing in the pellet mill are used for animal feed (agrifeed), pet food, fish food (aquafeed, aquaculture), etc. Each pellet will have close to the same characteristics in size, moisture content and nutritional value.