Cyclone X Multicyclone X Baghouse Filter X Filter Bag Cleaning X Electrostatic Precipitator X Spark Detection Extinguish X Abort Gate X Rotary Air Lock X Dust Collecting - Low Pressure:
 Cyclone Particle laden air enters through the inlet. The high turbulence breaks the heavier and lighter materials apart. The spinning air throws the heavier materials outward to the cyclone walls. Airflow on the cyclone walls is slowed by friction. Heavier particles get trapped in the slower moving air and gravity slowly pulls these heavier particles down. These heavier particles continue to slide downward and eventually exit out through an air lock. Near the bottom of the cone is a reversal point where the spinning air without the heavier particles reverses direction. That cleaned air then spirals up through the center of the cyclone then exits through the cyclone outlet. 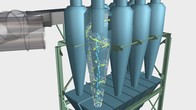 Multicyclone The dust laden air enters into the multiclone through the intake collector linking the tangential air intakes of the cyclones. The centrifugal action of each cyclone causes the particles to fall into a common hopper where they are exited through an air lock. The clean air is evacuated into the atmosphere.  Baghouse Filter Particle laden air enters through the high entry inlet. This incoming air strikes the baffle plates, causing the heavier material to fall to the bottom hopper. The air with the lighter and smaller materials is filtered by the bags and clean air is exhausted to atmosphere. The collected material is discharged from the system through an airlock to be collected in a conveying system.  Filter Bag Cleaning Air is pulsed through jets into the interior of the bags. This action causes the bag to ripple, knocking off the "cake" from the outside of the bag.  Electrostatic Precipitator Particles are charged by the electrodes and adhere to the collector plates in the electrostatic precipitator. Electro-mechanical rappers dislodge the particulate from the electrodes and collector plates. The rappers are located external to the ESP. Inlet and outlet distribution plates (not shown) ensure even distribution of flue gas over the collector plates.  Spark Detection Extinguish The system detects sparks in the duct air stream. When a preset quantity of sparks are detected, a signal will be sent to the extinguishing system. If the sparks reach a higher preset level, a signal will be sent to the abort gate to divert the material to atmosphere and shut down the processing equipment.  Abort Gate The abort gate will automatically open with a signal form the spark detection system indicating fire in the ductwork. With the abort gate open the material is diverted to atmosphere to prevent the material with sparks or burning embers from entering the baghouse filter. The processing equipment is shut down while the fans run for a set amount of time to allow the ducts to clear any hazards. The abort gate requires manual resetting.  Rotary Air Lock Air locks and rotary airlock systems allow material (chips, sawdust) to pass from a cyclone or baghouse to a bin or high pressure feeder. The air lock maintains a tight, positive air seal. The rotor has rubber or metal tips (vanes) that seal against the end plates and the housing. As the rotor turns, material drops between the vanes and are carried around to the bottom to be discharged. The vanes restrict the amount of air drawn up into the system preventing unwanted turbulence. | ||


